Cerebellar tonsil ectopia measurement in type I Chiari malformation patients show poor inter-operator reliability.
Fluids Barriers CNS. 2018 Dec 17;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12987-018-0118-1.
Lawrence BJ, Urbizu A, Allen PA, Loth F, Tubbs RS, Bunck AC, Kröger JR, Rocque BG, Madura C, Chen JA, Luciano MG, Ellenbogen RG, Oshinski JN, Iskandar BJ, Martin BA.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Type 1 Chiari malformation (CM-I) has been historically defined by cerebellar tonsillar position (TP) greater than 3-5 mm below the foramen magnum (FM). Often, the radiographic findings are highly variable, which may influence the clinical course and patient outcome. In this study, we evaluate the inter-operator reliability (reproducibility) of MRI-based measurement of TP in CM-I patients and healthy controls.
METHODS:
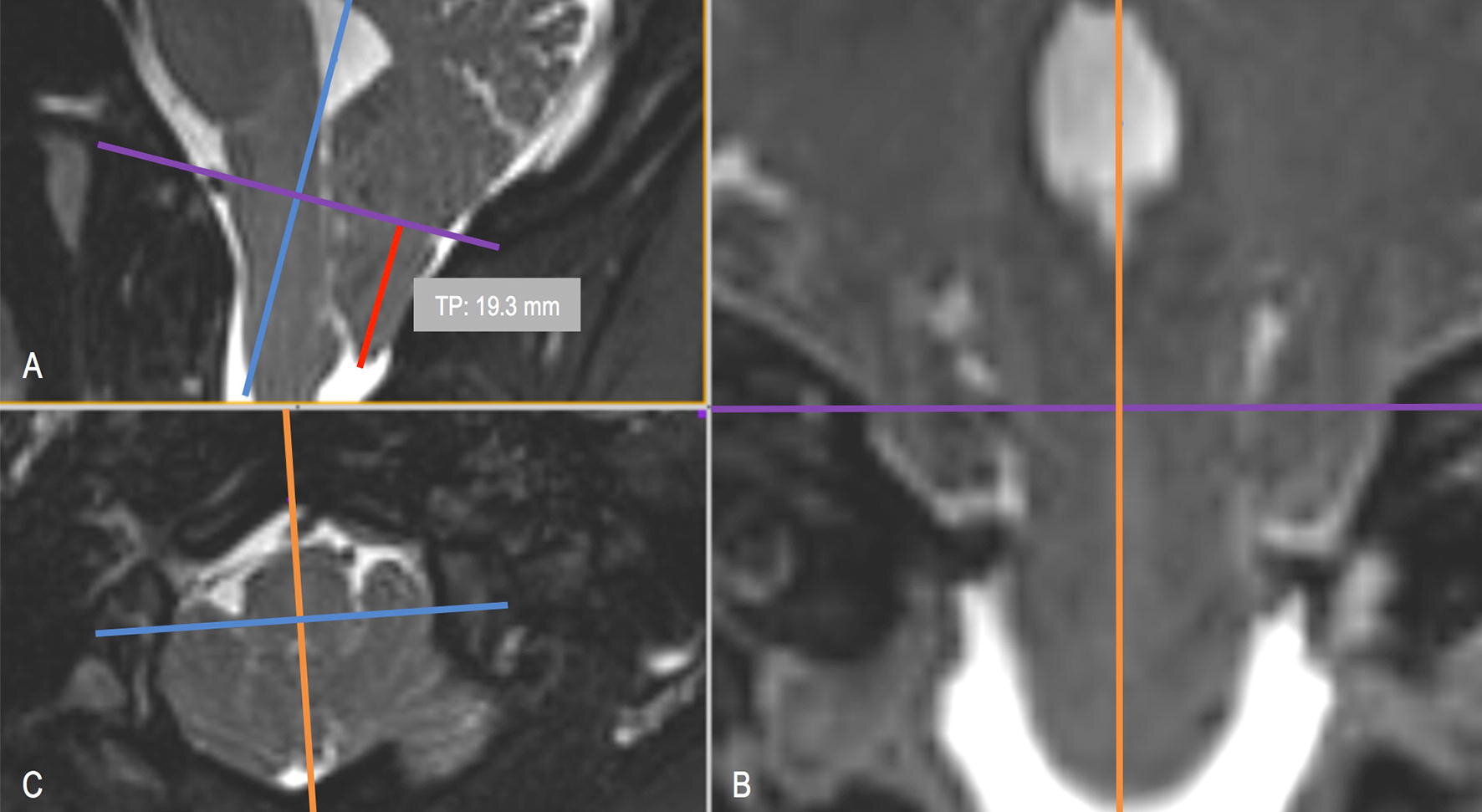
Thirty-three T2-weighted MRI sets were obtained for 23 CM-I patients (11 symptomatic and 12 asymptomatic) and 10 healthy controls. TP inferior to the FM was measured in the mid-sagittal plane by seven expert operators with reference to McRae's line. Overall agreement between the operators was quantified by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
RESULTS:
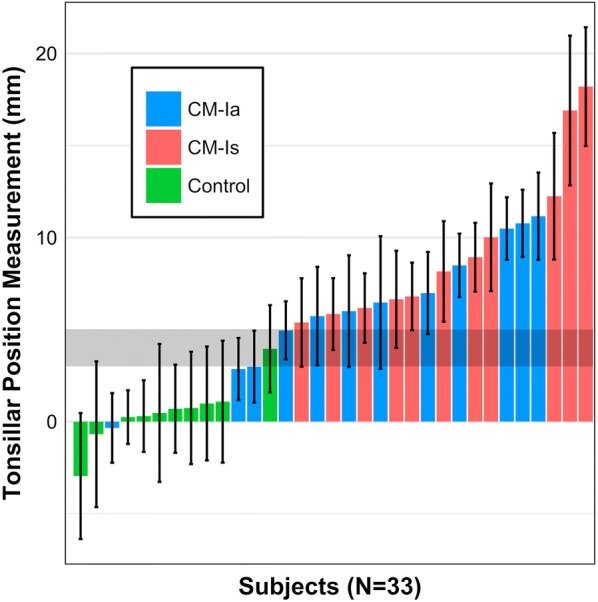
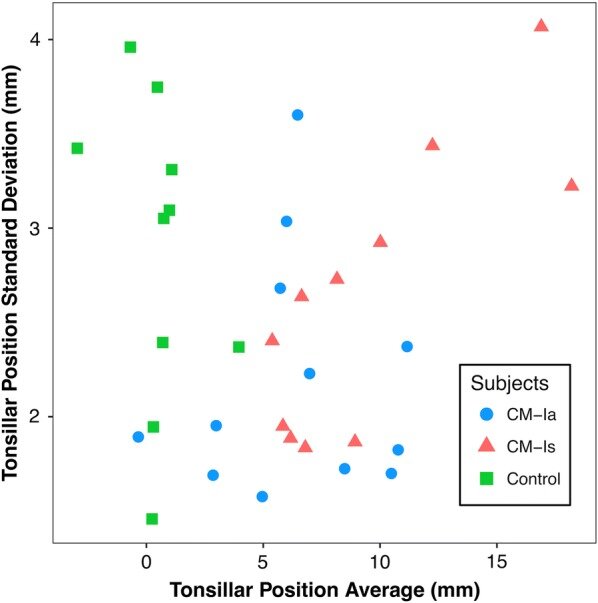
The mean and standard deviation of cerebellar TP measurements for asymptomatic (CM-Ia) and symptomatic (CM-Is) patients in mid-sagittal plane was 6.38 ± 2.19 and 9.57 ± 2.63 mm, respectively. TP measurements for healthy controls was 0.48 ± 2.88 mm. The average range of TP measurements for all data sets analyzed was 7.7 mm. Overall operator agreement for TP measurements was relatively high with an ICC of 0.83.
CONCLUSION:
The results demonstrated a large average range (7.7 mm) of measurements among the seven expert operators and support that, if economically feasible, two radiologists should make independent measurements before radiologic diagnosis of CM-I and surgery is contemplated. In the future, an objective diagnostic parameter for CM-I that utilizes automated algorithms and results in smaller inter-operator variation may improve patient selection.
KEYWORDS:
Cerebellar tonsil; Inter-operator reliability; MRI; Morphometric; Syringomyelia; Type 1 Chiari malformation