Abstract
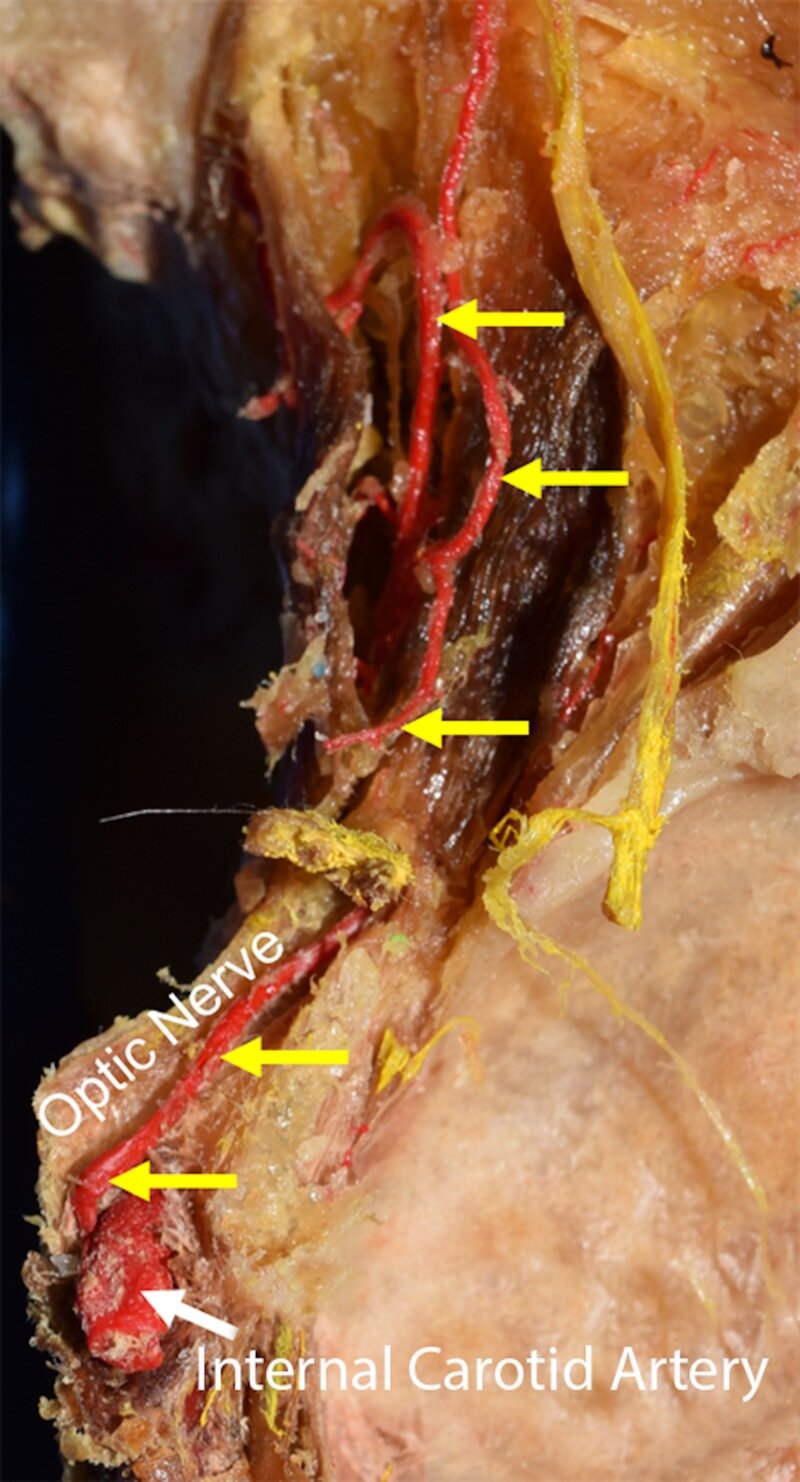
The ophthalmic artery arises from the supraclinoid segment of the internal carotid artery (ICA) and enters the orbit through the optic canal. It perfuses the orbit and the orbit apparatus. Ophthalmic artery aneurysms (OAA) account for 0.5% to 11% of all intracerebral aneurysms. Patients are usually asymptomatic but, in some cases, patients can present with ophthalmoplegia and total blindness if these aneurysms rupture. Aneurysms are usually diagnosed using computed tomography (CT) angiography but can also be seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and four-vessel digital subtraction angiography. Treatment of OAA entails either surgical or endovascular approaches with the mortality rate for surgical treatment as high as 25%, whereas embolization with balloon therapy is deemed safer with mortality rates around 9%. Recent techniques of embolization coiling have had even better results.
KEYWORDS:
aneurysm; embolization; ophthalmic artery; ophthalmoplegia